Motive (Impulse) Waves
Rules (these are “hard” rules; they cannot be broken)
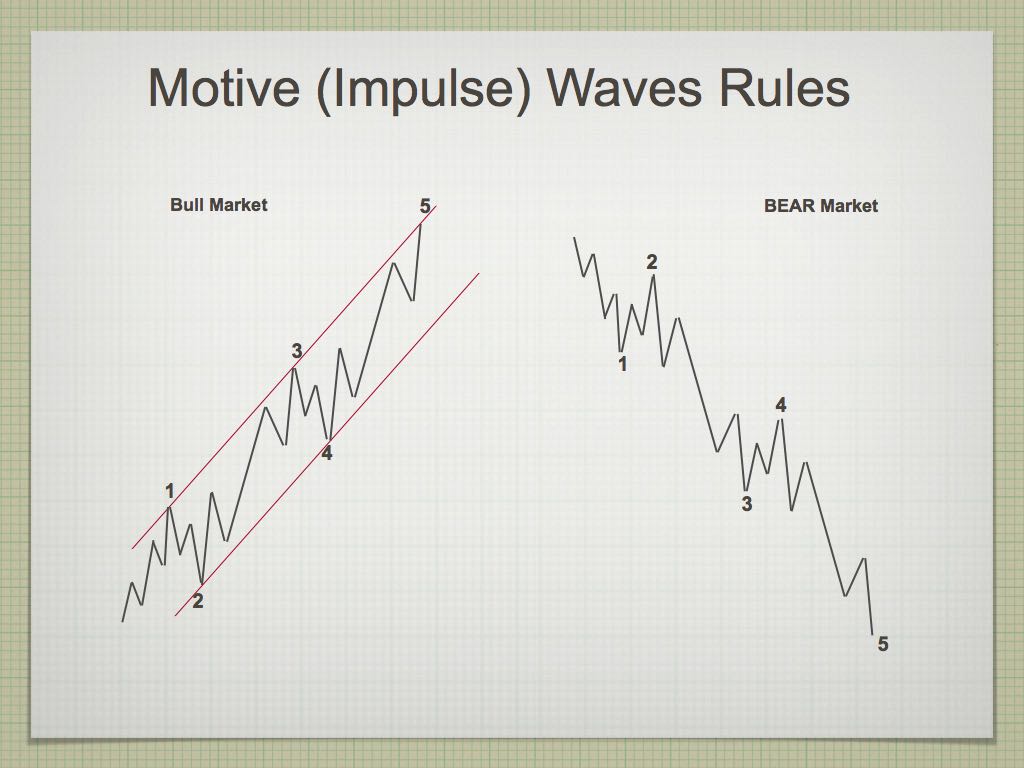
- An impulse always subdivides into five waves.
- Wave 1 always subdivides into an impulse or (rarely) a diagonal triangle.
- Wave 3 always subdivides into an impulse.
- Wave 5 always subdivides into an impulse or a diagonal ttiangle.
- Wave 2 always subdivides into a zigzag. flat or combination.
- Wave 4 always subdivides into a zigzag. flat. triangle or combination.
- Wave 2 never moves beyond the start of wave L
- Wave 3 always moves beyond the end of wave 1.
- Wave 3 is never the shortest wave.
- Wave 4 never moves beyond the end of wave L
- Never are waves 1, 3 and 5 all extended.
Guidelines (guidelines can be broken but it’s rare that they are)
- Wave 4 will almost always be a different corrective pattem than wave 2.
- Wave 2 is usually a zigzag or zigzag combination.
- Wave 4 is usually a flat, triangle or flat combination.
- Wave 5 often ends when meeting or slightly exceeding a line drawn from the end of wave 3 that is parallel to the line connecting the ends of waves 2 and 4 on either arithmetic or semilog scale.
- The center of wave 3 almost always has the steepest slope of any equal period within the parent impulse except that sometimes an early portion of wave 1 (the “kickoff” ) will be steeper.
- Wave 1, 3 or 5 is usually extended. (An extension appears “stretched”‘ because its corrective waves are small compared to its impulse waves. It is substantially longer, and contains larger subdivisions, than the non-extended waves).
- Often, the extended subwave is the same number (1, 3 or 5) as the parent wave.
- Rarely do two subwaves extend, although it is typical for waves 3 and 5 both to extend when they are of Cycle or Supercycle degree and within a fifth wave of one degree higher.
- Wave 1 is the least commonly extended wave.
- When wave 3 is extended, waves 1 and 5 tend to have gains related by equality or the Fibonacci ratio.
- When wave 5 is extended. it is often in Fibonacci proportion to the net travel of waves 1 through 3.
- When wave 1 is extended. it is often in Fibonacci proportion to the net travel of waves 3 thorough 5.
- Wave 4 typically ends when it is within the price range of sub wave four of 3.
- Wave 4 often subdivides the entire impulse into Fibonacci proportion in time and/or price.



